Quick and Easy Buying Guide
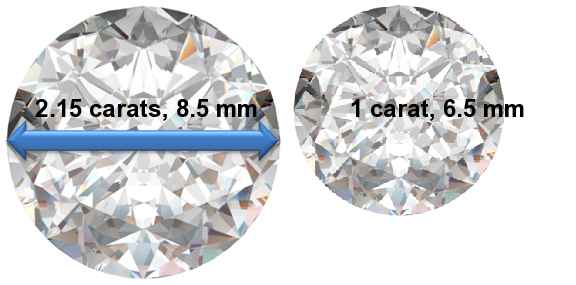
Carat weight: 1 carat = 200 milligrams = 6.5 mm diameter. Doubling weight doesn't double diameter.
Diamond clarity: FL/IF/VVS/VS = super expensive, near perfect. SI = best value if you can check a photo for obvious inclusions (defects).
Color: D-G = colorless, expensive, only if you have money to burn. H-J = best value. Can go lower in gold metal settings than white metal.
Cut: Better cut ratings let more light into a diamond, making it sparkle more. Very important property, don't skimp here.
Set a budget and minimum cut (Premium). Go J color for gold and I/H for white metals. Go searching for SI1/SI2 clarity diamonds at James Allen. Pick a diamond with small/no inclusions. Choose a ring setting and buy it risk-free (60-day returns).
2.15 Carat Diamonds
If you're interested in the normal metric weight of a 2.15 carat diamond, it is 430 mg. Diamond size means both the carat weight of the diamond and the width of the diamond, and the width of the diamond increases at a much slower rate compared to the carat weight of the diamond.
Sponsored Links
No gold-digging for me... I take diamonds! We may be off the gold standard someday. Mae West .
Looking around the internet at online diamond stores, you may be tempted to think that a four or five carat diamond is large. You couldn't be more wrong - the golden jubilee diamond is an example of how big diamonds can really be - it is 545 carats, or a weight of more than 100 g, which is about a quarter of the weight of a can of coke.
A large diamond which has a huge crack down the middle, or alternatively a big yucky looking inclusion, is not a good look - it looks like someone has gone for size and sacrificed all the other desirable properties of the diamond. Clarity, for example, can be just as important in picking a diamond.